 树
树
# 树:一种分层数据的抽象模型
# 构建方法
利用Object和Array构建树
# 深度/广度优先遍历
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支。
- 广度优先:先访问离根节点最近的节点。

# 二叉树
二叉树树中每个节点最多只能有两个节点,在JS中通常用Object来模拟二叉树。
# 先序遍历
# 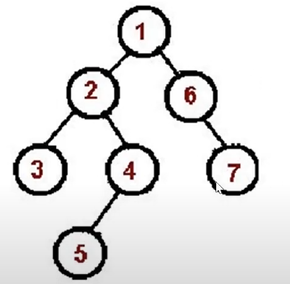
访问根节点
访问根节点的左子树进行先序遍历。
访问根节点的右子树进行先序遍历。
// 递归版前序遍历 const preorder = (root) => { console.log(root.val); prtorder(root.left); prtorder(root.right); } // 非递归版 const preorder = (root) => { if(!root) { return; } const stack = [root]; while(stack.length) { const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val) if(n.right) stack.push(n.right); if(n.left) stack.push(n.left); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 中序遍历:左根右
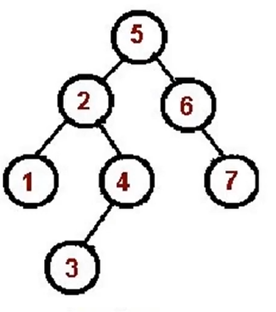
对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历。
访问根节点。
对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历。
// 递归版中序遍历 const inorder = root => { if(!root) return; inorder(root.left); console.log(rooot.val); inorder(root.right); } // 非递归版 const inorder = (root) => { if(!root) return; const stack = []; let p = root; while(stack.length || p) { while(p) { stack.push(p); p = p.left } const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); p = n.right } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 后续遍历:左右根
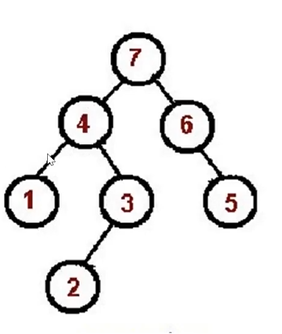
// 递归版本 const postorder = (root) => { if(!root) return; postorder(root.left); postorder(root.right); console.log(root.val); } // 非递归版 const postorder = (root) => { if(!root) return; const outputStack = []; const stack = [root]; while(stack.length) { const n = stack.pop(); outputStack.push(n); if(n.left) stack.push(n.left); if(n.right) stack.push(n.right); } while(outputStack.length) { const n = outputStack.pop(); console.log(n.val); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 案例
-
- 记录一个变量记录最大深度
- 利用深度遍历算法遍历二叉树。
- 深度优先遍历的过程中记录层级。
- 遍历过程中遇到孩子节点层数加一
- 刷新层级,对比最大深度和当前层级。
-
- 考虑使用广度优先遍历
- 过程中遇到叶子节点停止遍历,返回节点层级。
-
- 使用广度优先遍历;
- 遍历时需要记录当前节点所处的层级,方便将其添加到不同的数组中,
LeetCode:112 路径总和 (opens new window)
- 深度优先遍历
- 遍历过程中记录当前路径的节点值的和。
遍历JSON的所有节点值
const json = { a: { b: { c: 1 } } }; const dfs = (n, path) => { console.log(n, path); Object.keys(n).forEach(k => { dfs(n[k], path.concat(k)) }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
渲染Antd的树组件:深度优先遍历
# 🔚总结
树是一种分层数据的抽象模型;
树的常用操作;
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2022/02/21, 05:57:00